ICF-CY MedUse Practice Translator Coding Support Tool
Enter a search term
Search / Coding History
439 hits found for -1" OR 3*2<(0 5 327-327) -- in search historyOrder:
|
Back to search |
Browsing ICF-CY Code | Show complete ICF-CY Code |
| for: -1" OR 3*2<(0 5 327-327) -- |
 =Select (and add) this code =Select (and add) this code  =Browse from root node =Browse from root node 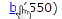 Click on a code to expand the branch Click on a code to expand the branch |
| ICFCY-Code | Title | Description | |
| < | |||
| b (550) | BODY FUNCTIONS | description | |
| b5 (76) | CHAPTER 5 FUNCTIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE, METABOLIC AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS | This chapter is about the functions of ingestion, digestion and elimination, as well as functions involved in metabolism and the endocrine glands and the growth maintenance functions. | |

|
b510 (16) | Ingestion functions | Functions related to taking in and manipulating solids or liquids through the mouth into the body. |

|
b5100 | Sucking | Functions of drawing into the mouth by a suction force produced by movements of the cheeks, lips and tongue. |

|
b5101 | Biting | Functions of cutting into, piercing or tearing off food with the front teeth. |

|
b5102 | Chewing | Functions of crushing, grinding and masticating food with the back teeth (e.g. molars). |

|
b5103 | Manipulation of food in the mouth | Functions of moving food around the mouth with the teeth and tongue. |

|
b5104 | Salivation | Function of the production of saliva within the mouth. |

|
b5105 (5) | Swallowing | Functions of clearing the food and drink through the oral cavity, pharynx and oesophagus into the stomach at an appropriate rate and speed. |

|
b5106 (1) | Vomiting | Functions of moving food or liquid in the reverse direction to ingestion, from stomach to oesophagus to mouth and out, such as in gastro-esophegeal reflux, recurrent vomiting, pyloric stenosis. |

|
b5107 | Ruminating | Functions of maintaining and manipulating vomit in the mouth. |

|
b5108 | Ingestion functions, other specified | |

|
b5109 | Ingestion functions, unspecified | |
| s (329) | BODY STRUCTURES | ||
| d (570) | ACTIVITIES AND PARTICIPATION | ||
| e (273) | ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS |