ICF-CY MedUse Practice Translator Coding Support Tool
Enter a search term
Search / Coding History
11 hits found for gelenk in search historyOrder:
| Hits | ICFCY-Code | Search Term |
| 11 | b710
 |
gelenk |
| 8 | b7102
 |
gelenk |
| 8 | b7108
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | s73021
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | b7109
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | b780
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | b7102
 |
bewegung gelenk |
| 7 | b7100
 |
bewegung gelenk |
| 7 | b540
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | b28016
 |
gelenk |
| 7 | b715
 |
gelenk |
|
Back to search |
Browsing ICF-CY Code | Show complete ICF-CY Code |
| for: gelenk |
 =Select (and add) this code =Select (and add) this code  =Browse from root node =Browse from root node 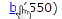 Click on a code to expand the branch Click on a code to expand the branch |
| ICFCY-Code | Title | Description | |
| < | |||
| b (550) | BODY FUNCTIONS | description | |
| b5 (76) | CHAPTER 5 FUNCTIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE, METABOLIC AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS | This chapter is about the functions of ingestion, digestion and elimination, as well as functions involved in metabolism and the endocrine glands and the growth maintenance functions. | |

|
b540 (6) | General metabolic functions | Functions of regulation of essential components of the body such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats, the conversion of one to another, and their breakdown into energy. |

|
b5400 | Basal metabolic rate | Functions involved in oxygen consumption of the body at specified conditions of rest and temperature. |

|
b5401 | Carbohydrate metabolism | Functions involved in the process by which carbohydrates in the diet are stored and broken down into glucose and subsequently into carbon dioxide and water. |

|
b5402 | Protein metabolism | Functions involved in the process by which proteins in the diet are converted to amino acids and broken down further in the body. |

|
b5403 | Fat metabolism | Functions involved in the process by which fat in the diet is stored and broken down in the body. |

|
b5408 | General metabolic functions, other specified | |

|
b5409 | General metabolic functions, unspecified | |
| s (329) | BODY STRUCTURES | ||
| d (570) | ACTIVITIES AND PARTICIPATION | ||
| e (273) | ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS |